Why Is Mannitol Salt Agar Used As A Selective Medium For Normal Skin Microbiota?
Mannitol salt agar (MSA) is a selective, differential, and indicator medium used to isolate and place Staphylococcus aureus from the clinical specimen. As its name suggests, mannitol salt agar (MSA) contains 1% mannitol (sugar), seven.v% salt, and agar as a solidifying agent. Members of the genus Staphylococcus tin tolerate high salt concentration (7.v%) and grow on mannitol common salt agar.
Principle
Mannitol salt agar (MSA) is a selective and differential medium.

Image source: ASM
Selective medium
Incorporating 7.5% sodium chloride in the medium helps select only those bacteria that can tolerate high table salt concentrations. Staphylococci species can tolerate this salt concentration, but other pathogenic bacteria may not. This concentration inhibits the growth of nigh other gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Thus MSA selectively isolates Staphylococcus spp i.e. selective media for Staphylococcus spp.
Differential Medium
Pathogenic staphylococci, i.e. Staphylococcus aureus is able to ferment mannitol, but coagulase-negative staphylococci (CONS) are not. So, if that detail specimen contains S. aureus, it ferments mannitol and changes the pH of the medium to acidic. As MSA contains phenol carmine as a pH indicator, at pH levels beneath 6.9, the medium is a yellow color. Simply if CONS grow, they cant ferment mannitol, then the color of the media effectually the bacterial colony does non alter to yellow; it appears pink. So, MSA is also a differential medium.
Remember that in the neutral pH (6.9 to 8.4) the color of phenol blood-red is crimson; while above pH 8.four, the colour of phenol red is pink. Other normally used media that comprise Phenol cerise as pH indicator are; TSI Agar, urea base of operations agar, and XLD agar.
Composition of Mannitol Salt Agar
- Enzymatic digest of casein (source of nitrogen, vitamin, and carbon)
- Enzymatic digest of animal tissue (source of nitrogen, vitamin, and carbon)
- Beef extract (source of nitrogen, vitamin, and carbon)
- D-Mannitol: Only carbohydrate source present in the medium
- Sodium chloride
- Phenol red (pH indicator)
- Agar
Final pH: seven.4 ± 0.ii at 25 oC
Training of Mannitol Common salt Agar
You can buy prepared mannitol common salt agar from commercial suppliers, go the powder, and prepare the media in your laboratory. Mannitol table salt agar is best prepared from ready-to-use dehydrated powder, available from near suppliers of civilisation media. The medium is usually used at xi.1 thou in every 100 ml of distilled water (concentration may vary depending on the manufacturer).
- Set up the medium equally instructed by the manufacturer. Sterilize by autoclaving at 121oC for xv minutes.
- When the medium has cooled to 50-55oC, mix well, and dispense it aseptically in sterile Petri dishes. Date the medium and give it a batch number.
- Shop the plates at 2-8oC in plastic bags to prevent moisture loss.
Shelf life: Several weeks, providing in that location is no change in the appearance of the medium to suggest contamination, deterioration, or alteration of pH.
The medium's pH should be within the range of pH 7.3 to seven.7 at room temperature.
Staphylococcus saprophyticus (coagulse-negative Staphylococci) may ferment mannitol, producing yellow halo around colonies in MSA thus resembling S. aureus.
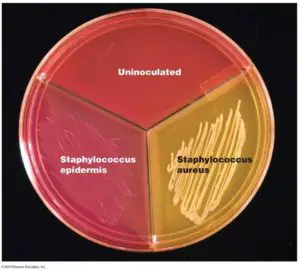
Colony Characteristics in Mannitol Salt Agar
- Escherichia coli: Does not grow
- Staphylococcus epidermidis: Colorless to pinkish colonies
- Staphylococcus aureus: Xanthous colonies; may take a yellow halo effectually colonies.
Annotation: Do not perform coagulase exam from the colonies isolated from mannitol table salt agar.
Troubleshooting
- When grown on mannitol salt agar, some Micrococcus (Micrococcus is a normal flora of human skin, mucosa, and oropharynx), such equally Chiliad. luteus (yellow) can produce yellow colonies. M. roseus (red) produces pink colonies on MSA. Find out the divergence between Micrococcus and Staphylococcus here
- Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium(the most common enterococcal species that accept been isolated from man infections) are salt-tolerant bacteria. They can ferment mannitol and produce lactic acid, producing yellowish-colored colonies on MSA. Catalase test tin can help to differentiate between Enterococcus (-ve) and Staphylococcus (+ve).
Recent Posts
Bunsen Burner: Parts, Principle, and Application
Bunsen burner is a gas burner that produces smokeless, nonluminous flame used for heating, sterilizing, and combustion purposes in laboratory experiments. It was named subsequently Robert Bunsen, a German...
Why Is Mannitol Salt Agar Used As A Selective Medium For Normal Skin Microbiota?,
Source: https://microbeonline.com/mannitol-salt-agar-msa-composition-uses-and-colony-characteristics/
Posted by: jostviong1977.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Why Is Mannitol Salt Agar Used As A Selective Medium For Normal Skin Microbiota?"
Post a Comment